ハーフメタル強磁性体とトンネル磁気抵抗効果
TMR and Half-Metals
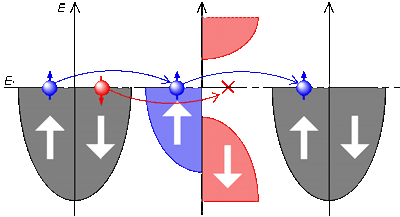 ハーフメタル強磁性体/非磁性体/ハーフメタル強磁性体という3層接合においては、右図のようにマジョリティースピンのみが伝導します. これはハーフメタル強磁性体においてはマイノリティー電子にのみバンドギャップが存在するためで、巨大磁気抵抗効果(GMR)・トンネル磁気抵抗効果(TMR)共に大きな値が期待されます.
For a half-metallic ferromagnet/non-magnet/half-metallic ferromagnet junction, only one spin channel is reserved for electron transport as shown in the right figure. Because of this spin-filtering effect, the half-metals can become an ideal spin source for both ohmic and ballistic transport.
ハーフメタル強磁性体/非磁性体/ハーフメタル強磁性体という3層接合においては、右図のようにマジョリティースピンのみが伝導します. これはハーフメタル強磁性体においてはマイノリティー電子にのみバンドギャップが存在するためで、巨大磁気抵抗効果(GMR)・トンネル磁気抵抗効果(TMR)共に大きな値が期待されます.
For a half-metallic ferromagnet/non-magnet/half-metallic ferromagnet junction, only one spin channel is reserved for electron transport as shown in the right figure. Because of this spin-filtering effect, the half-metals can become an ideal spin source for both ohmic and ballistic transport.
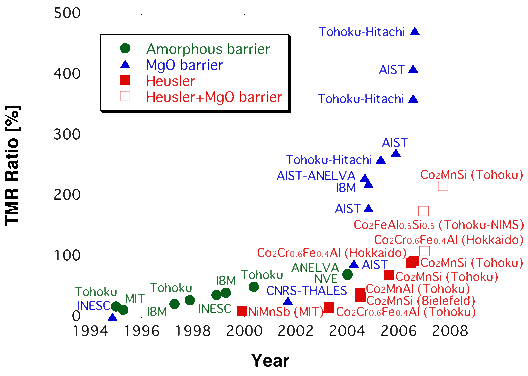 したがって理論上、ハーフメタル強磁性体を用いた強磁性トンネル接合は無限大のTMR比を示すことが期待されます. しかしながら現時点でこのような報告はなされていません. 左図の通りMgOトンネル障壁を用いたコヒーレントなトンネル伝導により、大きなTMR比が室温で報告されています. しかしハーフメタル強磁性体ではより小さなTMR比しか報告されていません. このような理論からの相違は界面の欠陥などに依るものと考えられ、ハーフメタル強磁性体のスピン分極率を大きく下げることが知られています. それゆえ界面の構造・磁性評価が重要となります.
In theory, a magnetic tunnel junction with half-metallic ferromagnets should therefore show infinite tnneling magnetoresistance (TMR). However, there has been no such a report presented to date As shown in the left figure, cherent tunneling through an epitaxial MgO barrier shows very large MR at room temperature RT), while the junctions with the half-metallic electrodes show much lower TMR ratios Tis departure from the theory is predominantly due to the interface disorder of the half-metals, hich is calculated to reduce the spin polarisation significantly It is therefore crucial to characterise the interfacial roperties and to find out a robust condition to maintainthe high spin polarisation at the interface.
したがって理論上、ハーフメタル強磁性体を用いた強磁性トンネル接合は無限大のTMR比を示すことが期待されます. しかしながら現時点でこのような報告はなされていません. 左図の通りMgOトンネル障壁を用いたコヒーレントなトンネル伝導により、大きなTMR比が室温で報告されています. しかしハーフメタル強磁性体ではより小さなTMR比しか報告されていません. このような理論からの相違は界面の欠陥などに依るものと考えられ、ハーフメタル強磁性体のスピン分極率を大きく下げることが知られています. それゆえ界面の構造・磁性評価が重要となります.
In theory, a magnetic tunnel junction with half-metallic ferromagnets should therefore show infinite tnneling magnetoresistance (TMR). However, there has been no such a report presented to date As shown in the left figure, cherent tunneling through an epitaxial MgO barrier shows very large MR at room temperature RT), while the junctions with the half-metallic electrodes show much lower TMR ratios Tis departure from the theory is predominantly due to the interface disorder of the half-metals, hich is calculated to reduce the spin polarisation significantly It is therefore crucial to characterise the interfacial roperties and to find out a robust condition to maintainthe high spin polarisation at the interface.
さらに興味のある方はFor further reading