最終更新日:2025年3月28日
Last updated: 28/03/2025
スピントロニクスって何?
What Is Spintronics?
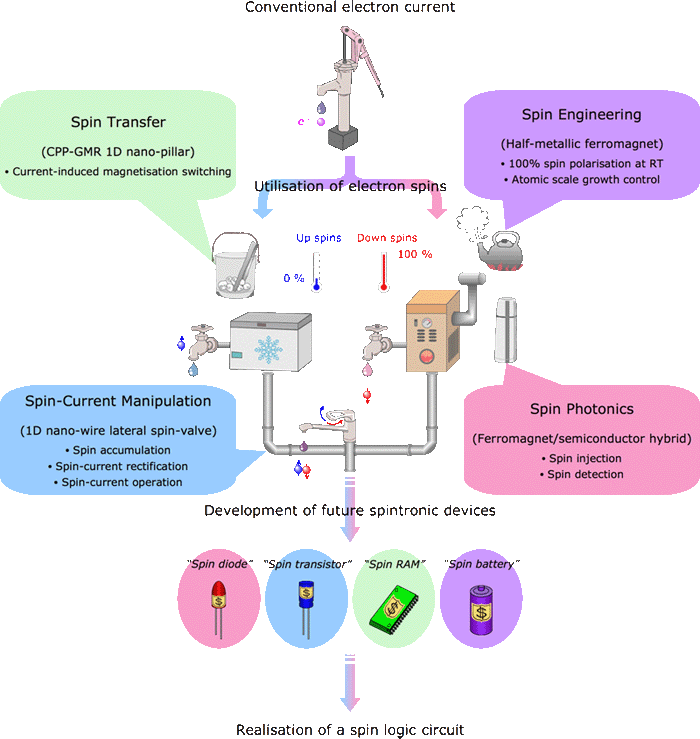 スピントロニクスは水に似ています. 昔は井戸水を使っていたように、これまでのエレクトロニクスでは電子の流れを扱ってきました. その後、水を凍らせたり沸騰させられるようになって、氷水や沸騰水を使えるようになりました. この2種類の水が温度0と100oCに対応しますので、左図のようにあたかも電子のスピンの割合が下向き0と100%のように扱うことができます.
Spintronics is similar to handling water in various forms. In early years, people have been used water from a well, which matches with a conventional electron current. Recently, we can either freeze or boil water, so that we can make use of either ice-cold or boiling-hot water. These two distinct forms of water are characterised by the temperature, 0 or 100oC, which corresponds to the electron-spin polarisation of 0 (up spins) or 100% (down spins) as shown in the figure.
スピントロニクスは水に似ています. 昔は井戸水を使っていたように、これまでのエレクトロニクスでは電子の流れを扱ってきました. その後、水を凍らせたり沸騰させられるようになって、氷水や沸騰水を使えるようになりました. この2種類の水が温度0と100oCに対応しますので、左図のようにあたかも電子のスピンの割合が下向き0と100%のように扱うことができます.
Spintronics is similar to handling water in various forms. In early years, people have been used water from a well, which matches with a conventional electron current. Recently, we can either freeze or boil water, so that we can make use of either ice-cold or boiling-hot water. These two distinct forms of water are characterised by the temperature, 0 or 100oC, which corresponds to the electron-spin polarisation of 0 (up spins) or 100% (down spins) as shown in the figure.
この温度差(とそれに対応するスピンの割合、スピン分極率)は氷水や沸騰水を混ぜ合わせることで自由に選べます. これまでは、私たちの周りにある磁石(鉄・コバルト・ニッケルなど)を使ってこうした割合を出してきましたが、完全に0または100oCの材料は膜としては使われていません. そこでこのように理想的なスピンの電池が必要なのです. Such temperature (or spin polarisation) differences can be introduced by boiling water for example (or atomically engineering spin configurations in a metal). Similarly, ferromagnets, such as Fe, Co and Ni, can induce a cetain degree of spin polarisation. Up to date, since there is no perfect spin source at room temperature, it is very important to create a new magnetic material, which has a 100% spin polarisation and can be utilised as a "spin battery."
生み出された低温または高温の水は、氷水や沸騰水として運ぶことができます. 同じようにスピン分極率も電流などによって運ぶことができて、電気や光として取り出すことができます. このようなスピンの移動と検出を使って計算などをしようというのがスピントロニクスです. The generated cold or hot water can be carried in the forms of ice or boiling vapor, and the temperature (spin polarisation) can be then transferred to other materials (spin transfer). The transferred spin polarisation can finally be taken out as an electrical voltage or light emission (spintronics or spin photonics). These phenomena enables us to produce a "spin memory" and a "spin diode."
このように好きな温度(スピン分極率)を選んで、混合水栓のようにスピンを取り扱うことができれば、より複雑な計算などができるようになります. Finally, both cold and hot water are mixed and the water temperature can be continuously tuned by a combined tap. Spin polarisation can be tuned in the same way in the near futue (spin manipulation), building a "spin transistor."